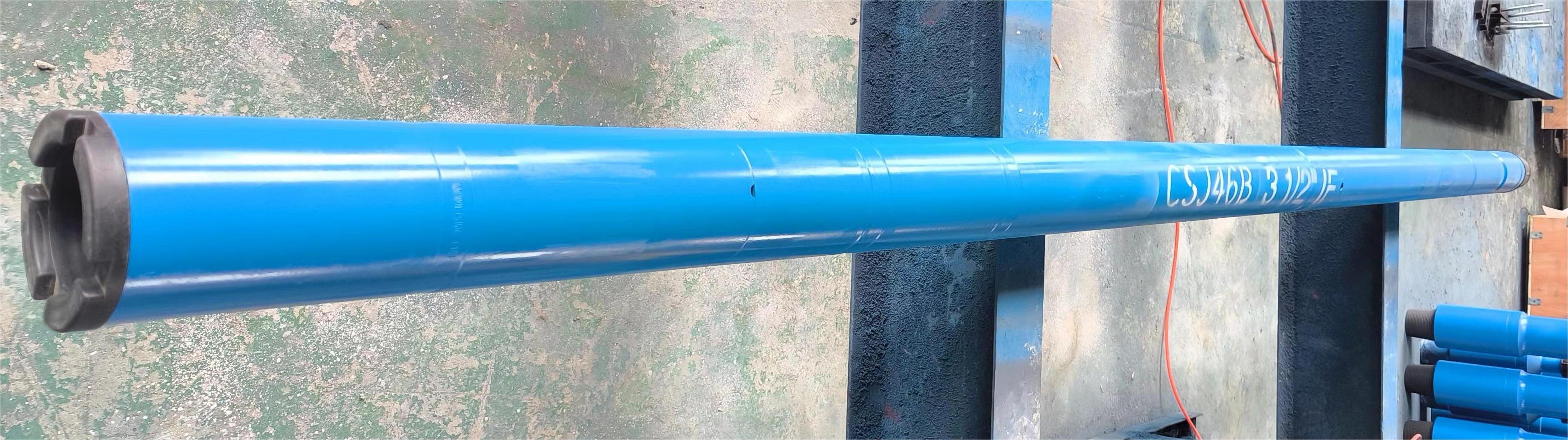
Boiler pipe
Product Parameters
Product Parameters
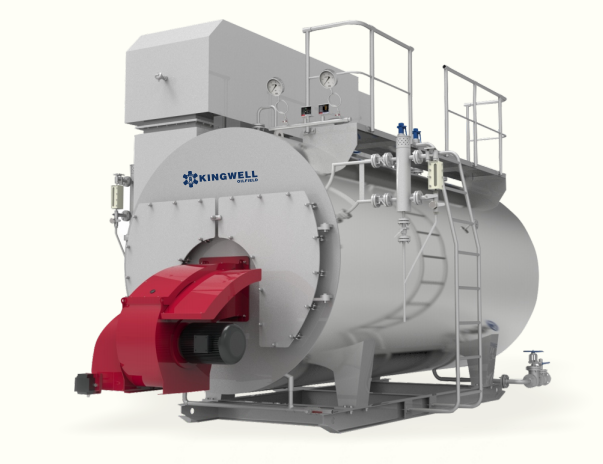
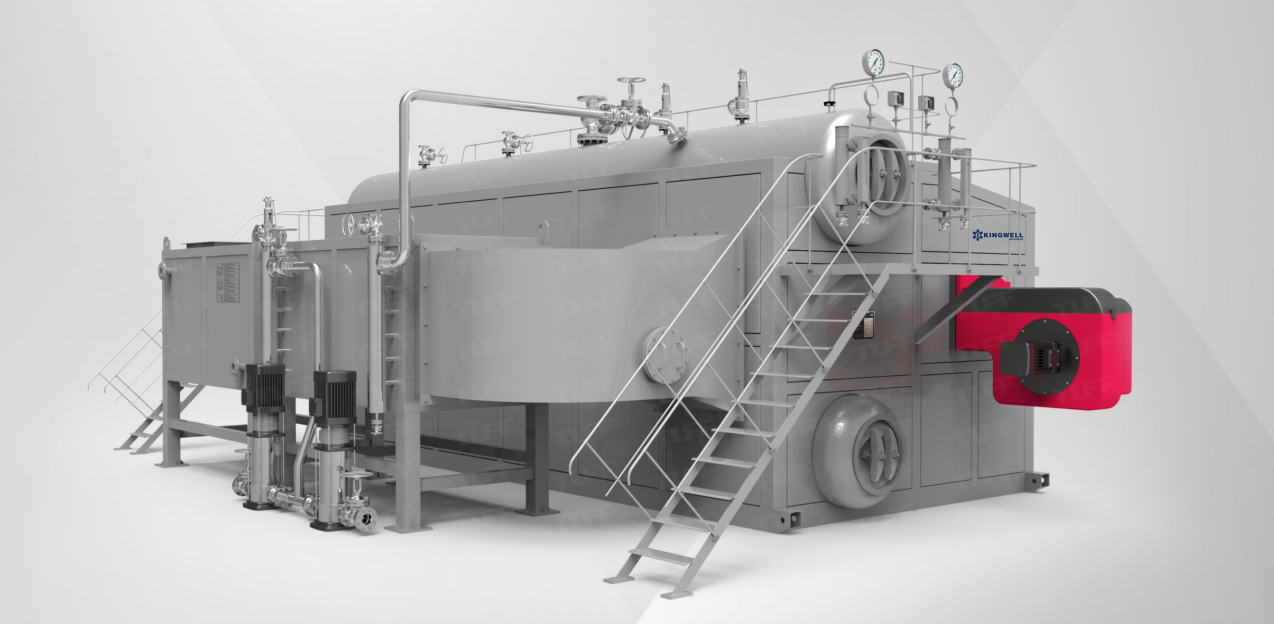
Boiler Pipe Description
Boiler pipes are critical components of boiler systems, categorized by function and structure as follows:
Water Tube: Located in the furnace, water flows inside the tubes while high-temperature flue gas heats the outer walls. Used for water walls, steam-generating tubes, and superheater tubes. Typical materials include 20G and 15CrMoG alloy steel, offering high-temperature/pressure resistance and corrosion resistance.
Smoke Tube/Flue Tube: Flue gas flows inside the tubes to heat the external medium, serving as a convective heating surface. Made of seamless steel pipes (e.g., φ63.5×3.5mm, Grade 10/20), with surface defects like cracks or folds strictly prohibited.
Header: Connects water-cooled wall tubes or smoke tubes for medium collection and distribution. Fabricated from seamless steel pipes (diameter ≥100mm) with hand holes at both ends for maintenance.
Downcomer: Transports water from the lower drum zone to headers, maintaining natural circulation. Insulated to reduce heat loss, typically made of 20G carbon steel.
Chimney Tube: Connects the furnace crown to the shell head, acting as a flue gas exhaust passage. Some sections lie in the steam space, requiring cast iron sleeves to prevent overheating deformation. Materials must resist high-temperature oxidation.
Material and Performance Requirements
High-pressure boiler tubes must withstand temperatures >450°C and pressures >15.7MPa, using high-alloy steels like P91/T92 with high creep strength and fatigue resistance.
Manufacturing involves hot rolling/cold drawing, normalizing/quenching heat treatment, and rigorous testing (hydrostatic test, ultrasonic inspection) per GB5310-2008.
Key performance metrics: tensile strength ≥410MPa, yield strength ≥245MPa, elongation ≥30%, hardness ≤156HB.
Applications
Widely used in power plant boilers (e.g., supercritical pressure boilers), industrial boilers (e.g., HRSG), and high-temperature/high-pressure systems in chemical/metallurgical industries for steam/water transport, heat exchange, and pressure bearing.

 Global Service Hotline +86-18729329559
Global Service Hotline +86-18729329559